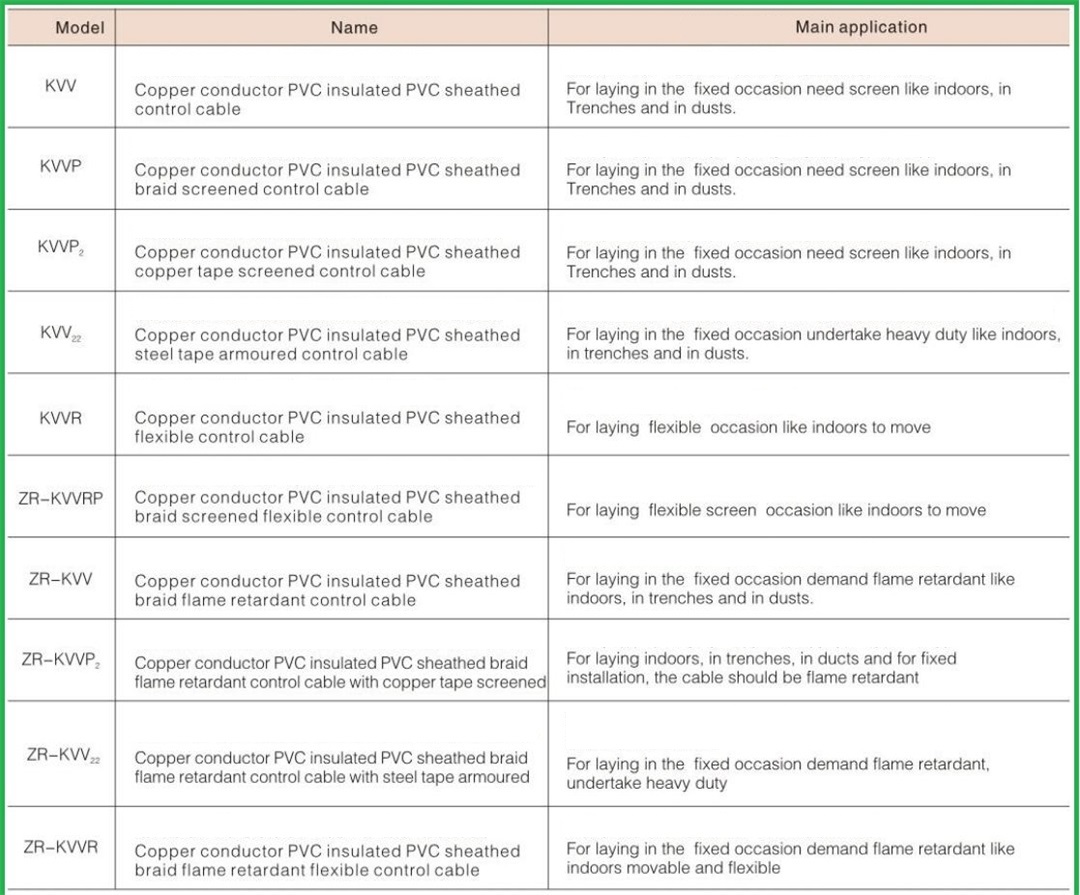
 KVV belongs to the control cable of cables used for electrical devices, which has good performance of high temperature resistance, cold resistance and aging resistance, and is generally used for controlling monitoring circuits and protecting circuits. In addition, manufacturers can produce flame-retardant, fire-resistant and low smoke zero halogen control cables according to user requirements. Different types of KVV cables have different characteristics and functions. 1. Flame retardant control cables are applicable to PVC insulated and PVC sheathed control cables used in industrial and mining enterprises, energy and transportation departments, control of AC rated voltage below 450/750 V, proximity and protection of lines. 2. The fire-resistant control cable has a high fire-resistant performance. Within a certain period of time, it will not experience short circuit and short circuit fault when it is directly burned by flame. This product is suitable for various occasions with high fire risk and high fire safety importance, and is used as the connecting line between electrical equipment and control system. 3. The low smoke halogen-free control cable has low smoke discharge when heated, and it is a thermoplastic or thermosetting composition that does not contain halogen, and is suitable for use as a control connecting line in densely populated and low air density situations.
KVV belongs to the control cable of cables used for electrical devices, which has good performance of high temperature resistance, cold resistance and aging resistance, and is generally used for controlling monitoring circuits and protecting circuits. In addition, manufacturers can produce flame-retardant, fire-resistant and low smoke zero halogen control cables according to user requirements. Different types of KVV cables have different characteristics and functions. 1. Flame retardant control cables are applicable to PVC insulated and PVC sheathed control cables used in industrial and mining enterprises, energy and transportation departments, control of AC rated voltage below 450/750 V, proximity and protection of lines. 2. The fire-resistant control cable has a high fire-resistant performance. Within a certain period of time, it will not experience short circuit and short circuit fault when it is directly burned by flame. This product is suitable for various occasions with high fire risk and high fire safety importance, and is used as the connecting line between electrical equipment and control system. 3. The low smoke halogen-free control cable has low smoke discharge when heated, and it is a thermoplastic or thermosetting composition that does not contain halogen, and is suitable for use as a control connecting line in densely populated and low air density situations.
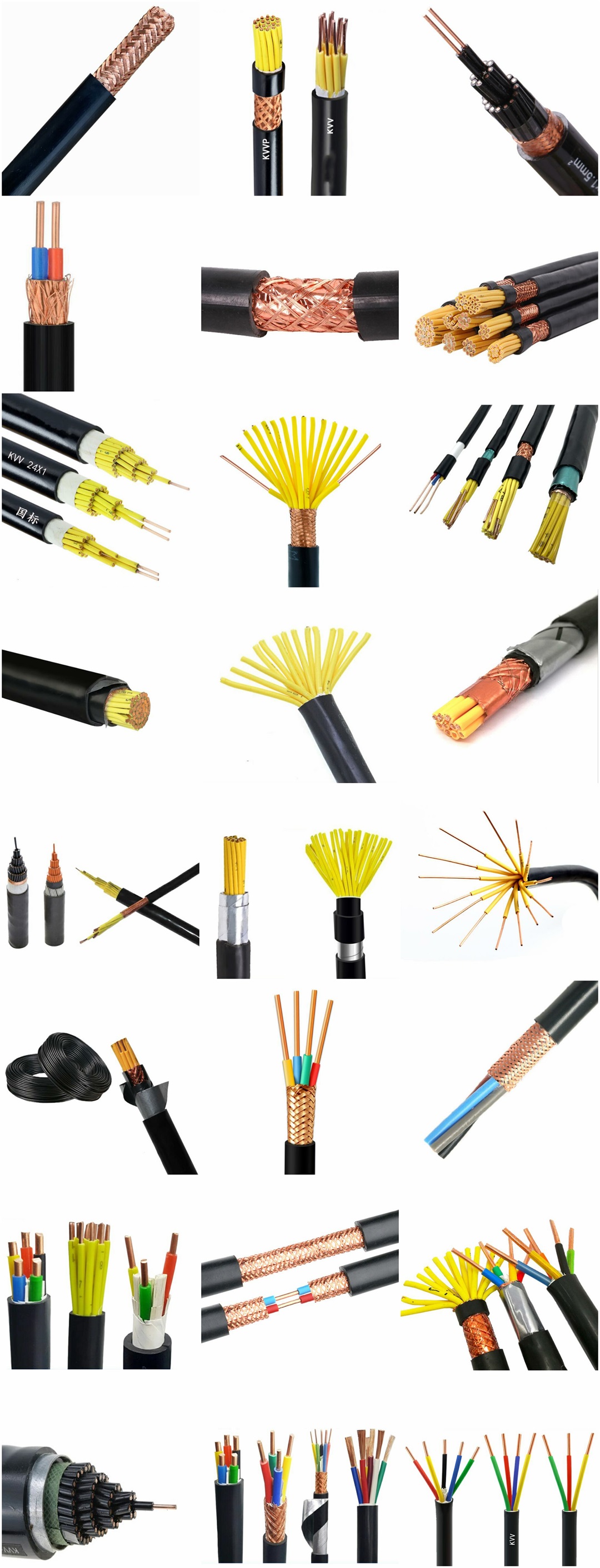





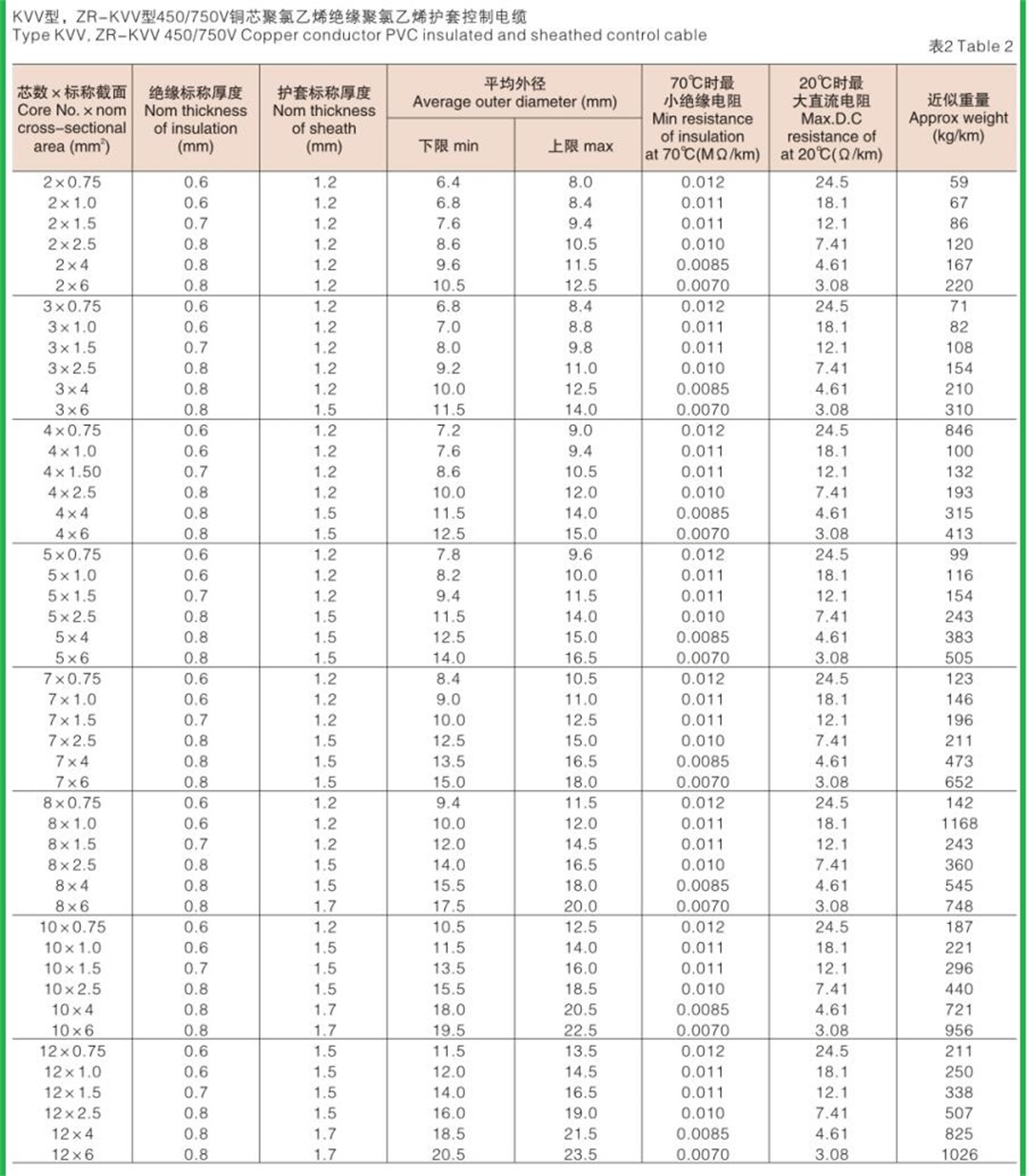
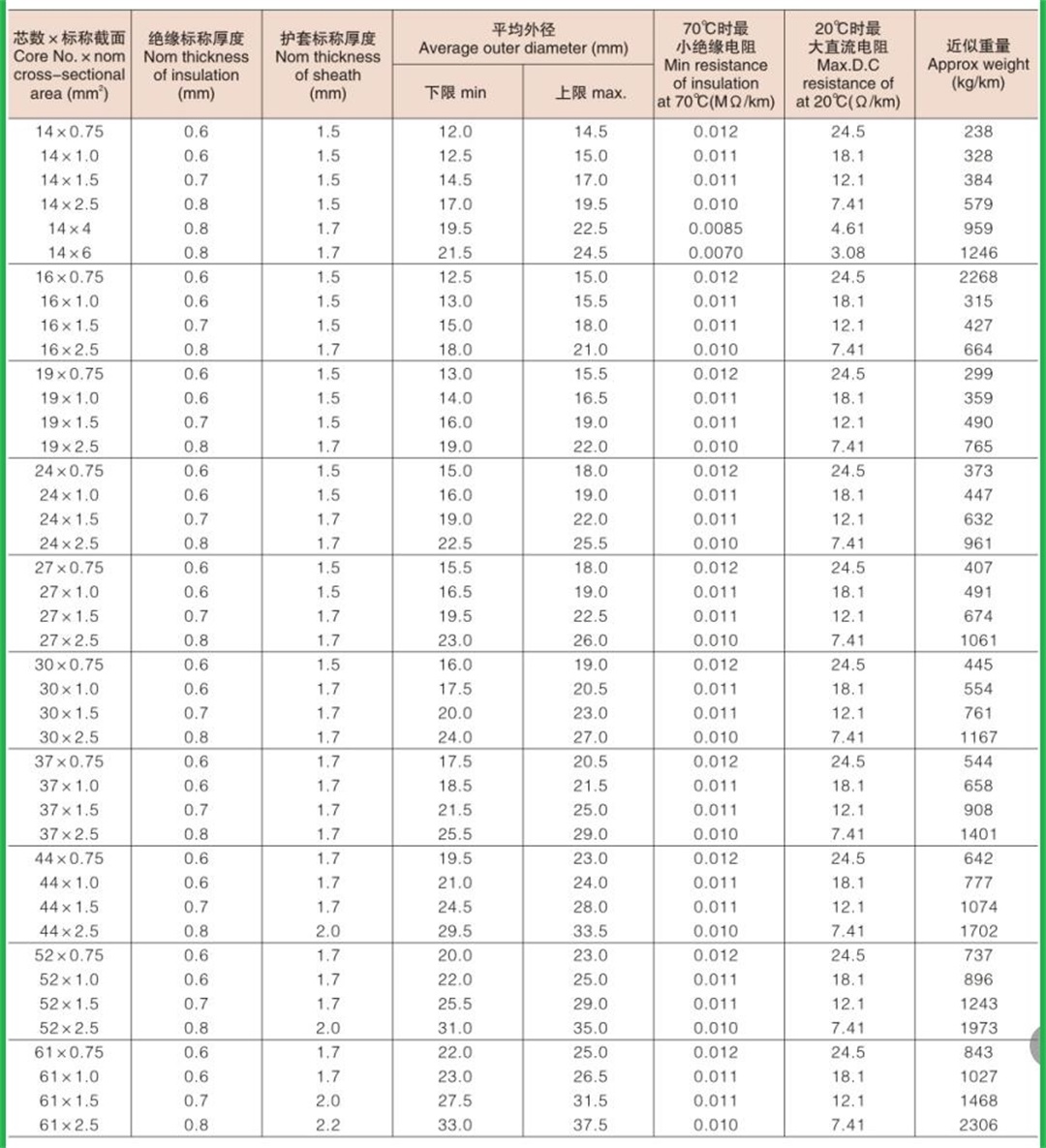
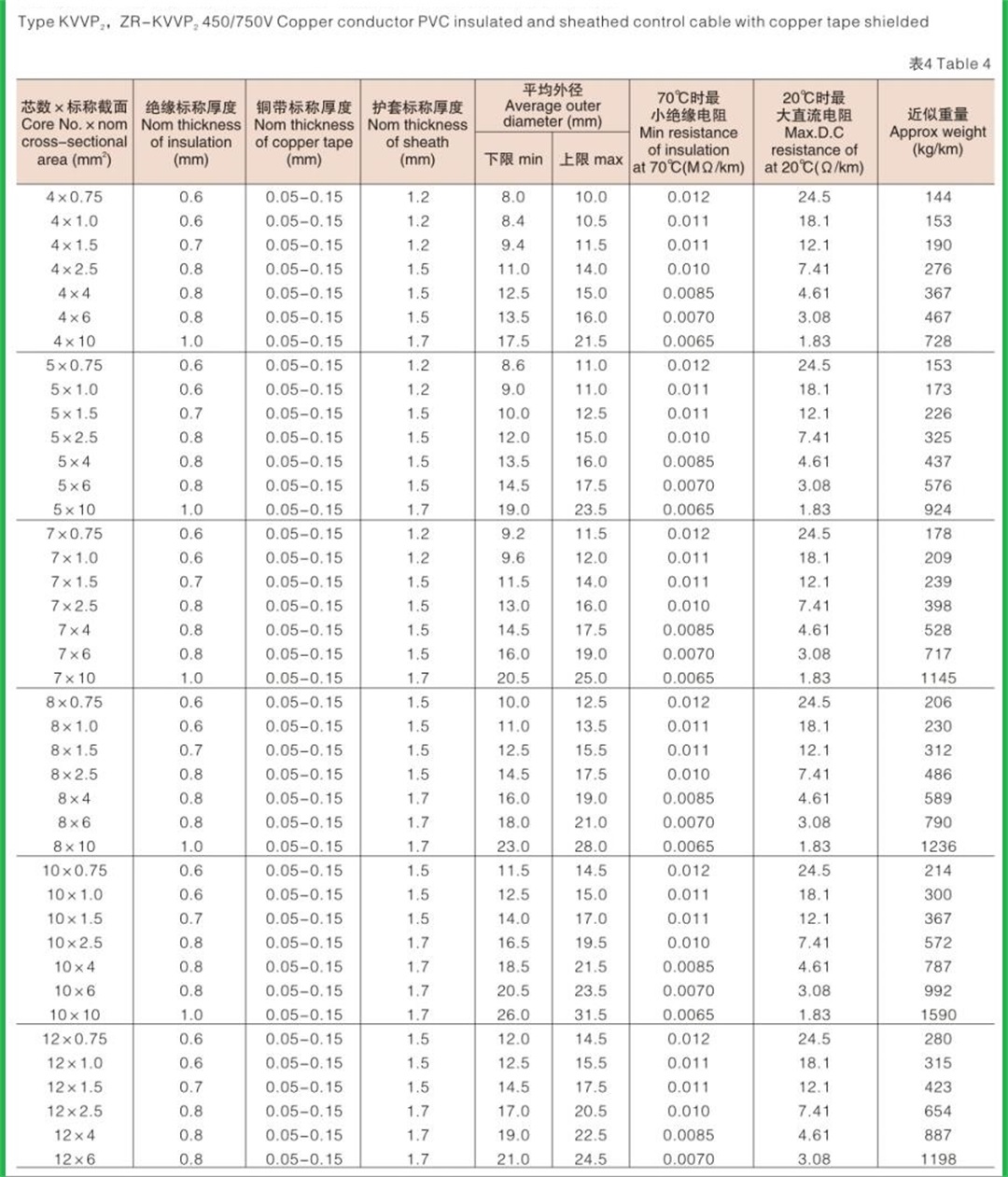
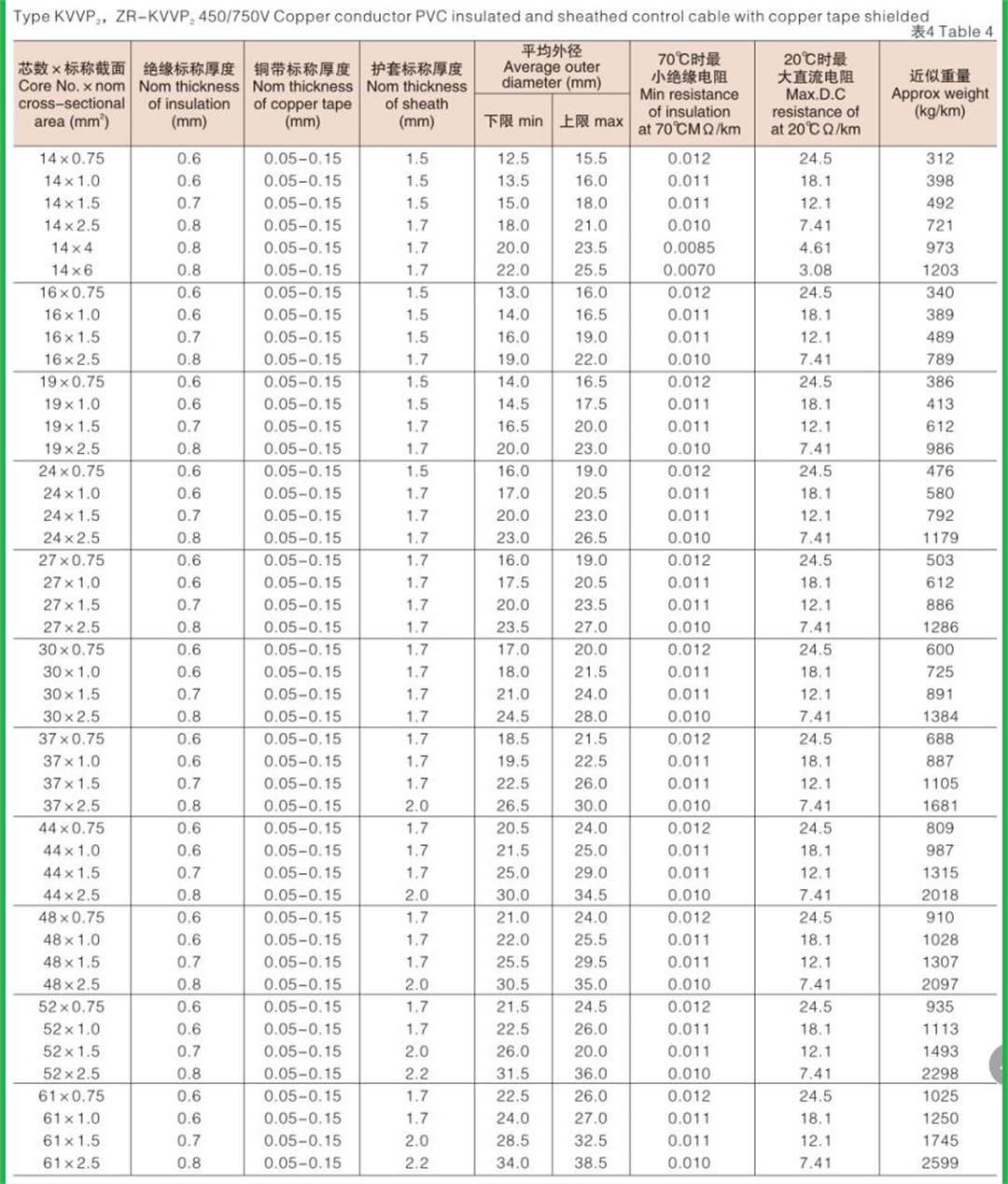
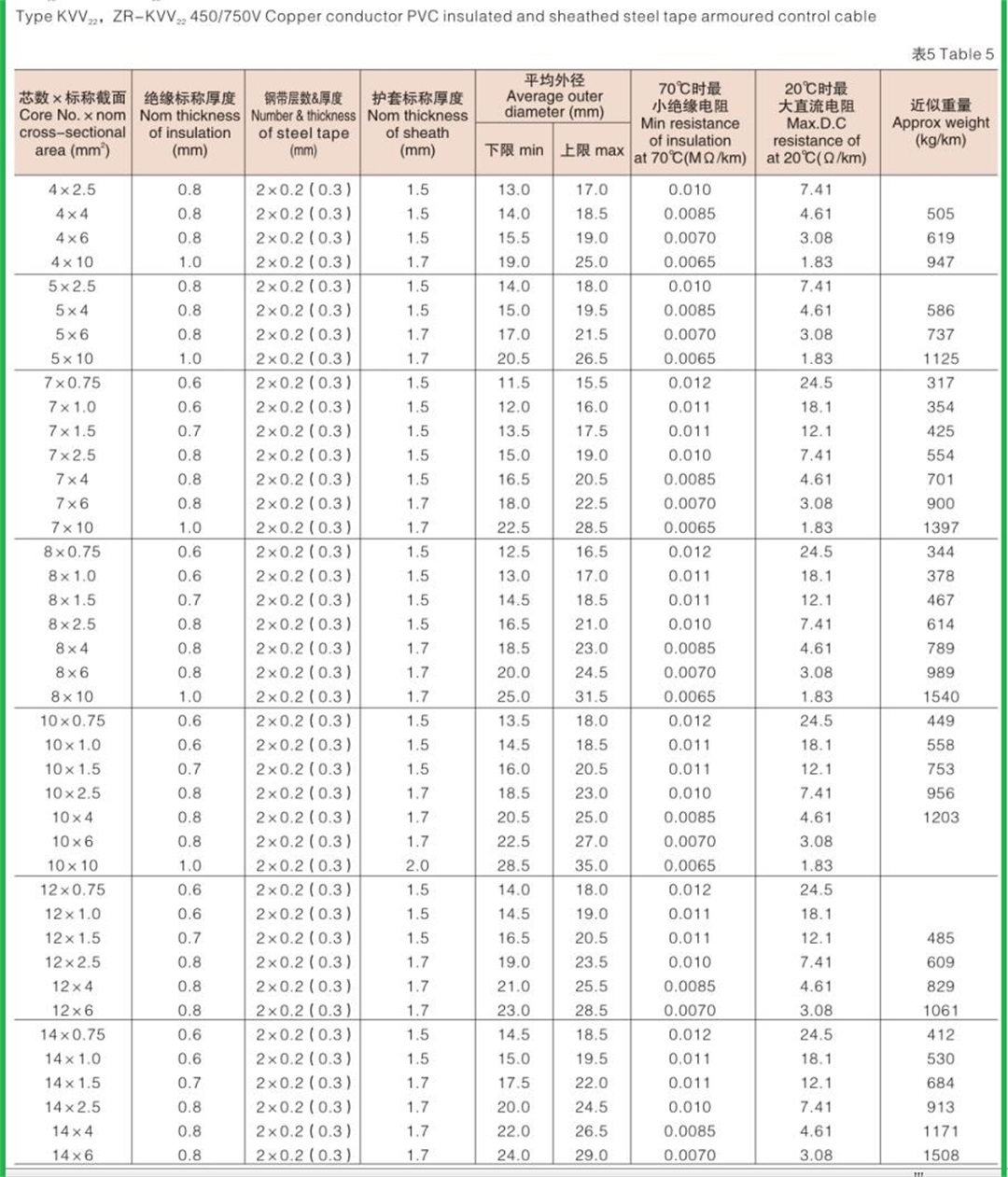
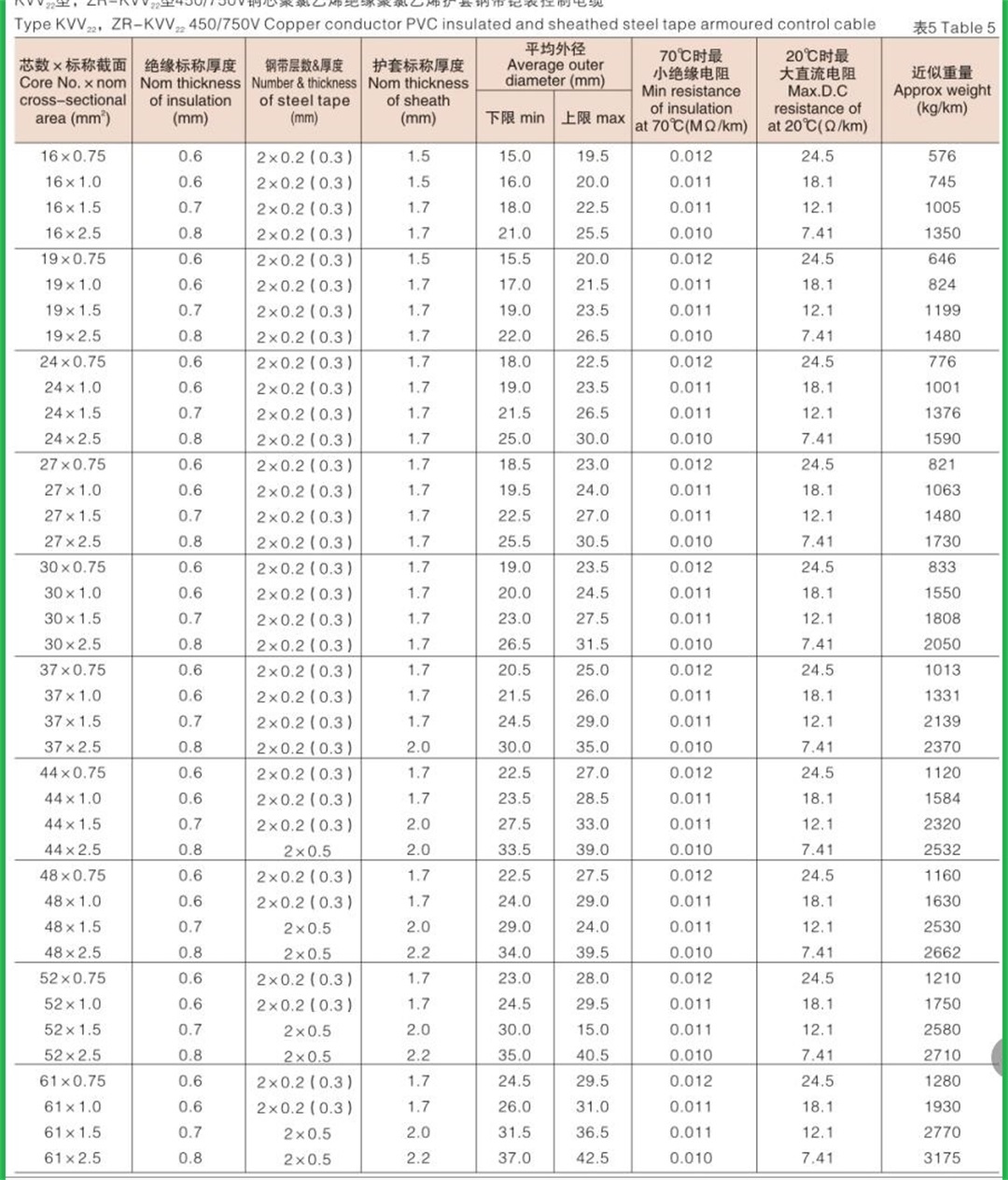
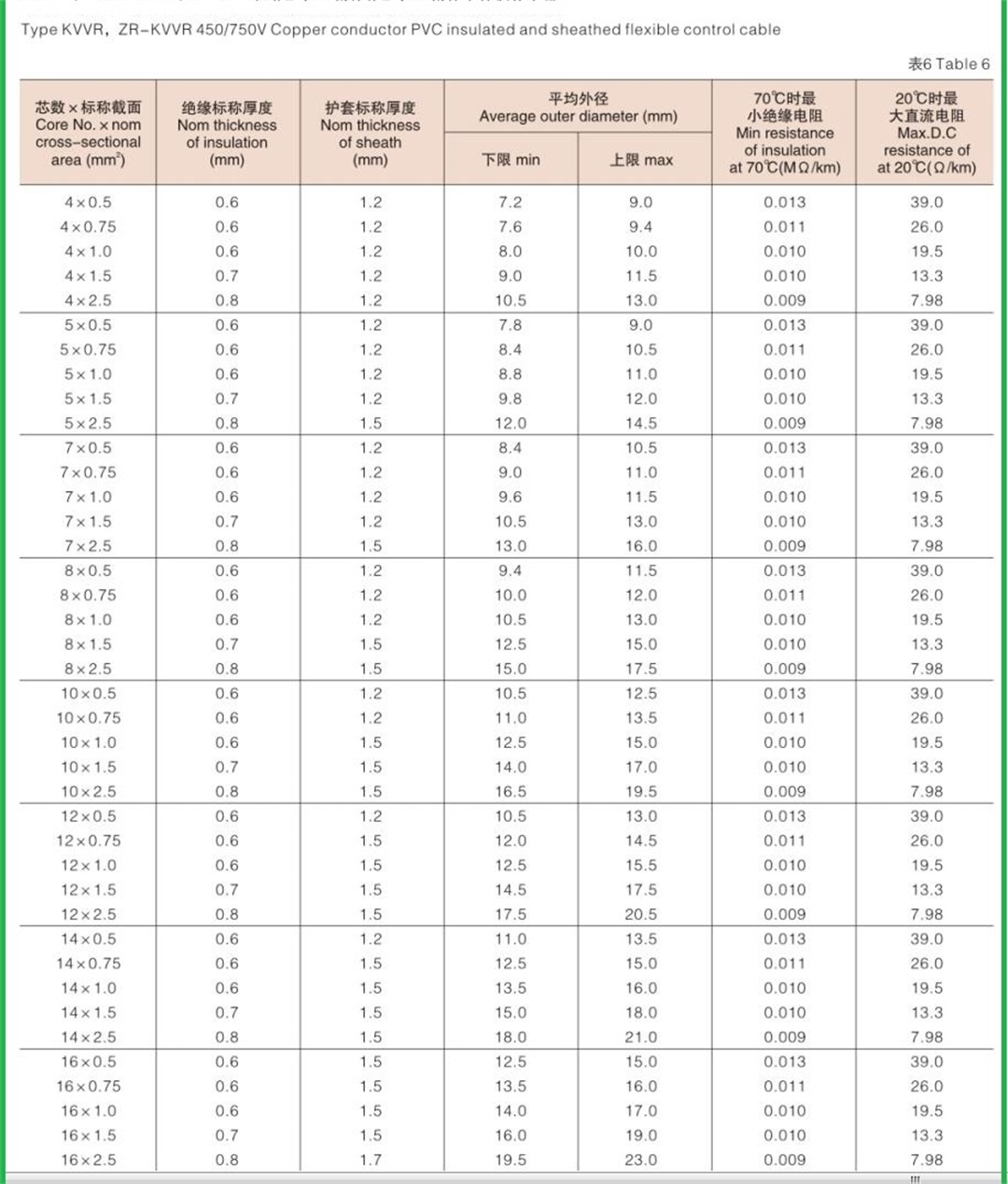
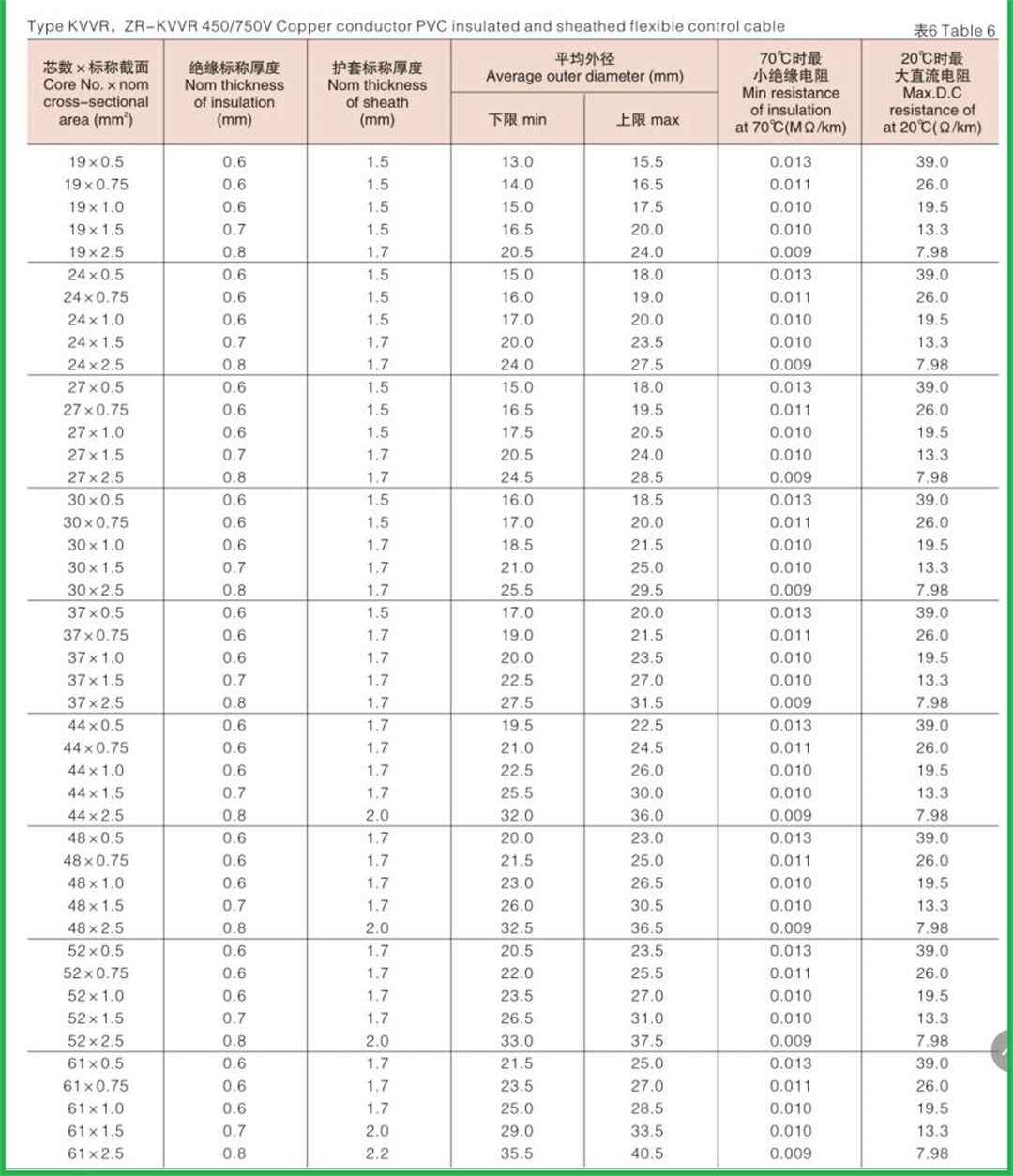
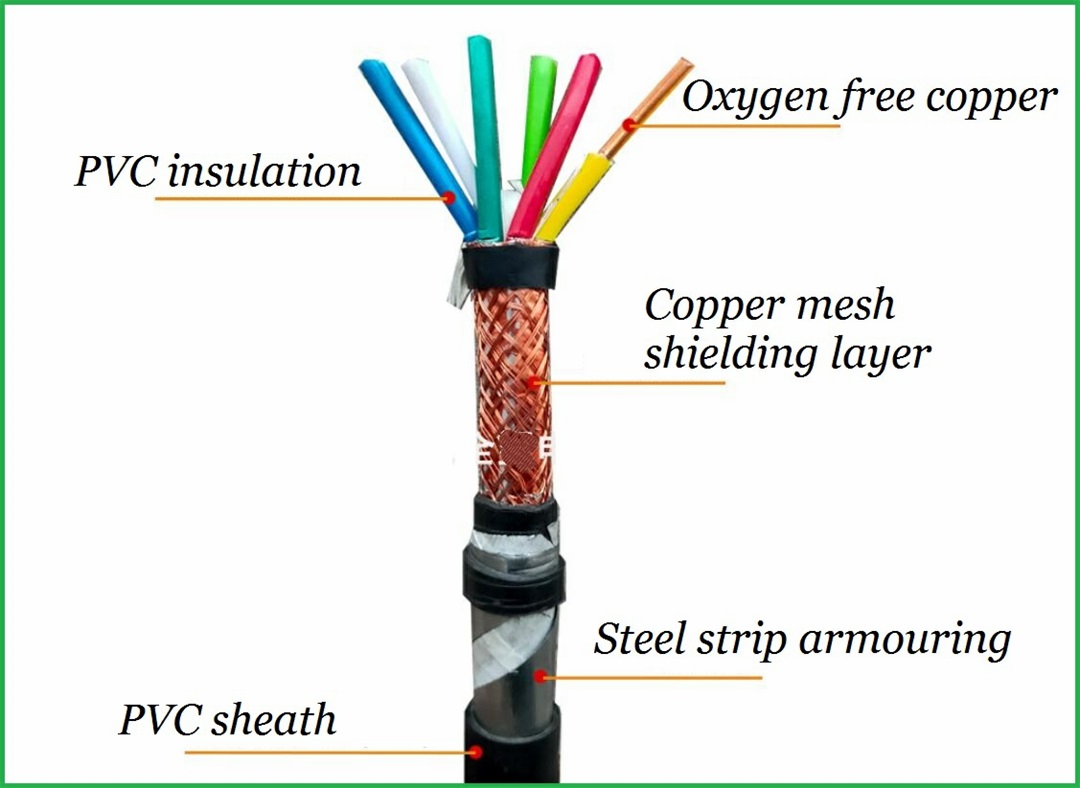
 Structure of KVV cable: Conductor: oxygen free copper Insulation: PVC insulation Sheath: flame retardant PVC sheath Standard: GB/T9330-2008 Basic characteristics of KVV cable: 1. The rated power frequency voltage Uo/U is 450/750V or 0.6/1kV; 2. The number of cores that can be produced is 2-61; 3. The maximum allowable long-term working temperature of cable conductor is 70 ℃; 4. The ambient temperature during cable laying shall not be lower than 0 ℃. If the ambient temperature is lower than 0 ℃, the cable shall be preheated; 5. The recommended allowable bending radius of cable is as follows: (1) The unarmoured cable shall not be less than 6 times of the outer diameter of the cable; (2) Armored or copper tape shielded cable shall not be less than 12 times of the cable outer diameter; (3) Shielded flexible cable shall not be less than 6 times of the cable outer diameter. 6. Cable KVV and KVVR structure: conductor insulation layer with sheath; 7. KVV control cables are widely laid indoors, in cable trenches, pipelines and other fixed places.
Structure of KVV cable: Conductor: oxygen free copper Insulation: PVC insulation Sheath: flame retardant PVC sheath Standard: GB/T9330-2008 Basic characteristics of KVV cable: 1. The rated power frequency voltage Uo/U is 450/750V or 0.6/1kV; 2. The number of cores that can be produced is 2-61; 3. The maximum allowable long-term working temperature of cable conductor is 70 ℃; 4. The ambient temperature during cable laying shall not be lower than 0 ℃. If the ambient temperature is lower than 0 ℃, the cable shall be preheated; 5. The recommended allowable bending radius of cable is as follows: (1) The unarmoured cable shall not be less than 6 times of the outer diameter of the cable; (2) Armored or copper tape shielded cable shall not be less than 12 times of the cable outer diameter; (3) Shielded flexible cable shall not be less than 6 times of the cable outer diameter. 6. Cable KVV and KVVR structure: conductor insulation layer with sheath; 7. KVV control cables are widely laid indoors, in cable trenches, pipelines and other fixed places.
